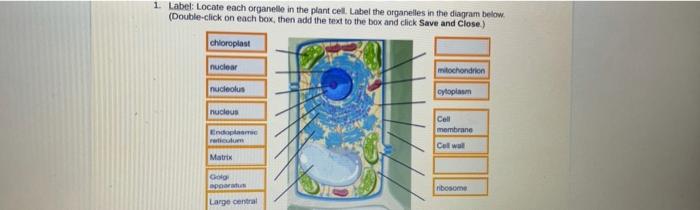
Locate each organelle in the plant cell, embarking on a fascinating journey into the intricate world of plant biology. From the protective cell wall to the energy-producing mitochondria, discover the essential structures that orchestrate the life of a plant cell.
Delve into the functions and compositions of each organelle, unraveling their vital roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis, photosynthesis, and growth. Witness the remarkable diversity of organelles, each uniquely adapted to specific tasks within the plant cell’s bustling metropolis.
Cell Wall
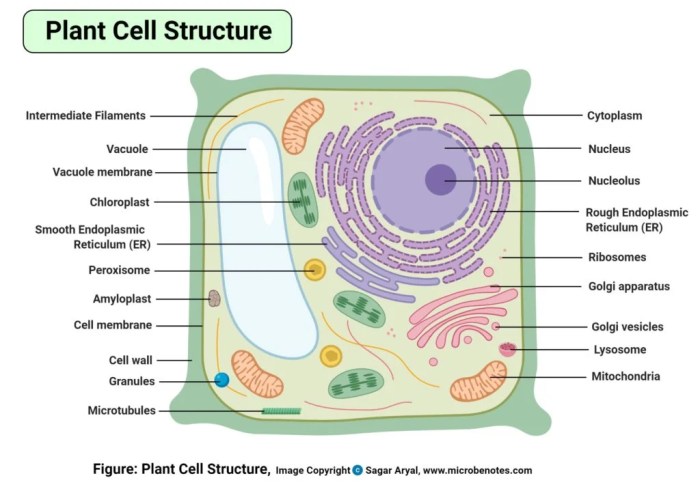
The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the plant cell membrane. It provides structural support and protection to the cell, and it also helps to regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
The cell wall is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. Cellulose is a strong, fibrous material that provides the cell wall with its strength. Hemicellulose is a branched polysaccharide that helps to cross-link the cellulose fibers. Pectin is a sticky substance that helps to hold the cell wall together.
Functions of the Cell Wall, Locate each organelle in the plant cell
- Provides structural support and protection to the cell
- Regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell
- Helps to maintain the cell’s shape
- Provides a barrier against pathogens
Differences in the Cell Wall of Different Types of Plant Cells
The cell wall of plant cells can vary in thickness and composition depending on the type of plant cell. For example, the cell walls of collenchyma cells are thicker and more rigid than the cell walls of parenchyma cells. The cell walls of xylem cells are lignified, which makes them even more rigid.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell. It acts as a barrier between the cell and its surroundings, and it regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads of the phospholipids face outward, while the hydrophobic tails face inward. This arrangement creates a barrier that is impermeable to most molecules.
Functions of the Cell Membrane
- Acts as a barrier between the cell and its surroundings
- Regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell
- Helps to maintain the cell’s shape
- Provides a site for cell signaling
How the Cell Membrane Regulates the Movement of Substances
The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which means that it allows some substances to pass through it while blocking others. The permeability of the cell membrane is determined by the structure of the phospholipid bilayer. Small, nonpolar molecules can easily pass through the cell membrane, while large, polar molecules cannot.
The cell membrane also contains proteins that can transport specific molecules across the membrane.
Cytoplasm: Locate Each Organelle In The Plant Cell
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell. It is composed of water, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and other molecules. The cytoplasm is the site of many cellular activities, including metabolism, protein synthesis, and cell division.
Functions of the Cytoplasm
- Provides a medium for cellular activities
- Stores nutrients and waste products
- Facilitates the movement of organelles within the cell
- Supports the cell membrane
Organelles Found in the Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm contains a variety of organelles, including:
- Nucleus
- Vacuoles
- Chloroplasts
- Mitochondria
- Ribosomes
- Golgi apparatus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
Popular Questions
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall provides structural support and protection for the plant cell.
What is the role of chloroplasts in photosynthesis?
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis, where sunlight is converted into energy-rich molecules.
How do mitochondria generate energy for the cell?
Mitochondria produce energy through cellular respiration, a process that converts glucose into ATP.