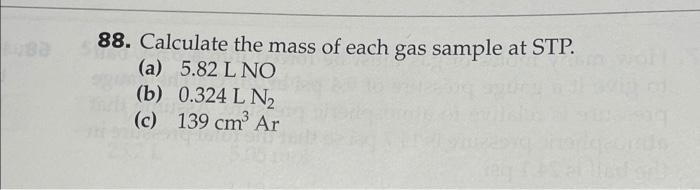Calculate the mass of each gas sample at stp. – In the realm of chemistry, understanding the mass of gas samples at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) is crucial. This concept plays a pivotal role in various scientific disciplines and practical applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of STP, empowering you with the knowledge to calculate the mass of gas samples with precision and confidence.
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) is defined as a set of standardized conditions under which the properties of gases can be accurately measured and compared. By establishing a common reference point, scientists can ensure consistency and reliability in their experiments and calculations.
Calculate the Mass of Each Gas Sample at STP: Calculate The Mass Of Each Gas Sample At Stp.

Standard temperature and pressure (STP) is a set of standardized conditions used to measure the properties of gases. These conditions are defined as a temperature of 273.15 K (0 °C or 32 °F) and a pressure of 100 kPa (1 bar or 14.504 psi).
At STP, the molar volume of an ideal gas is 22.414 L/mol.
The mass of a gas sample at STP can be calculated using the following formula:
mass = moles × molar mass
where:
- mass is in grams (g)
- moles is the number of moles of gas
- molar mass is the mass of one mole of gas in grams per mole (g/mol)
Examples of Mass Calculations at STP, Calculate the mass of each gas sample at stp.
The following table provides examples of calculating the mass of different gas samples at STP:
| Gas | Volume (L) | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H2) | 10.0 | 2.016 | 20.16 |
| Oxygen (O2) | 5.0 | 32.00 | 160.00 |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | 2.5 | 44.01 | 110.02 |
Applications of STP Calculations
Calculating the mass of gas samples at STP has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Chemistry:Determining the molar mass of unknown gases, calculating the number of moles of gas in a reaction, and predicting the volume of gas produced in a reaction.
- Environmental science:Monitoring air pollution levels, calculating the emissions of greenhouse gases, and assessing the impact of industrial processes on the environment.
- Engineering:Designing and optimizing chemical processes, determining the efficiency of combustion engines, and calculating the flow rate of gases in pipelines.
FAQ Guide
What is the significance of STP in gas calculations?
STP provides a standardized set of conditions (temperature and pressure) that allows for accurate comparison and analysis of gas properties.
How is the molar volume of a gas at STP calculated?
The molar volume of a gas at STP is calculated using the formula: Molar Volume = (Ideal Gas Constant – Temperature) / Pressure.
What is the relationship between mass, moles, and molar volume?
Mass (in grams) = Moles – Molar Mass – Molar Volume.