Delve into the fascinating realm of kinetic theory of gases worksheets, where the microscopic world unveils its secrets. These worksheets provide an interactive and engaging approach to understanding the fundamental principles governing the behavior of gases.
Kinetic theory of gases worksheets delve into the assumptions, principles, and applications of this theory, exploring its significance in real-world scenarios. By examining the relationship between kinetic energy and temperature, these worksheets shed light on the underlying mechanisms that drive the behavior of gases.
Introduction to Kinetic Theory of Gases
Kinetic theory of gases is a model that describes the physical behavior of gases on the atomic and molecular scale. It explains the properties of gases in terms of the motion of their constituent particles.
The kinetic theory of gases is based on the following assumptions:
- Gases are composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms or molecules.
- These particles are in constant random motion.
- The particles collide with each other and with the walls of their container.
- The average kinetic energy of the particles is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
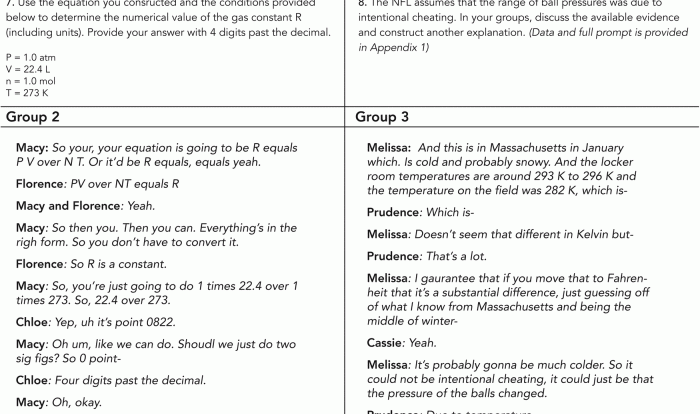
The relationship between kinetic energy and temperature is given by the following equation:
KE = (3/2)
- k
- T
Where:
- KE is the average kinetic energy of the particles.
- k is the Boltzmann constant.
- T is the absolute temperature of the gas.
Applications of Kinetic Theory of Gases
The kinetic theory of gases is a powerful tool that can be used to explain a wide variety of phenomena involving gases. It is based on the assumption that gases are composed of tiny, constantly moving particles. These particles are so small that they can be considered point masses, and they interact with each other only through elastic collisions.
The kinetic theory of gases can be used to explain a wide range of properties of gases, including their pressure, volume, temperature, and density. It can also be used to explain the behavior of gases in a variety of processes, such as diffusion, effusion, and heat transfer.
Examples of Applications
- The kinetic theory of gases can be used to explain the behavior of gases in a variety of everyday applications, such as the operation of refrigerators, air conditioners, and internal combustion engines.
- It can also be used to explain the behavior of gases in industrial processes, such as the production of chemicals and the refining of petroleum.
- The kinetic theory of gases is also used in the development of new technologies, such as fuel cells and microfluidics.
Limitations
The kinetic theory of gases is a very successful theory, but it does have some limitations. One limitation is that it does not take into account the effects of intermolecular forces. These forces can be significant for gases at high pressures or low temperatures.
Another limitation of the kinetic theory of gases is that it does not take into account the quantum nature of matter. This can be significant for gases at very low temperatures.
Activities and Experiments on Kinetic Theory of Gases
Demonstrating the kinetic theory of gases through activities and experiments can provide a hands-on and engaging approach to understanding the behavior of gases.
Diffusion and Effusion
- Diffusion:
Diffusion can be demonstrated by placing a drop of perfume in one corner of a room. The perfume molecules will gradually spread throughout the room, indicating the diffusion of gases.
- Effusion:
Effusion can be demonstrated using a Graham’s effusion apparatus. The apparatus consists of two bulbs connected by a narrow tube. One bulb is filled with a gas, and the other is evacuated. When the stopcock is opened, the gas will effuse through the narrow tube into the evacuated bulb.
The rate of effusion can be measured and compared for different gases, demonstrating the relationship between molecular mass and effusion rate.
Pressure and Volume
- Boyle’s Law:
Boyle’s law can be demonstrated using a syringe and a manometer. The syringe is filled with a gas, and the manometer is used to measure the pressure. When the volume of the gas is decreased by pushing the plunger, the pressure will increase, demonstrating Boyle’s law.
- Charles’s Law:
Charles’s law can be demonstrated using a flask filled with a gas and a thermometer. The flask is heated, and the temperature is measured. As the temperature increases, the volume of the gas will increase, demonstrating Charles’s law.
Temperature and Molecular Motion
- Brownian Motion:
Brownian motion can be observed using a microscope to view small particles suspended in a liquid or gas. The particles will exhibit random, erratic motion due to collisions with the surrounding gas molecules, demonstrating the kinetic nature of gases.
- Heat Conduction:
Heat conduction can be demonstrated by placing a metal rod over a flame. The heat from the flame will be conducted through the rod, causing the other end to become hot. This demonstrates the transfer of thermal energy through the collision of gas molecules.
Simulations and Visualizations on Kinetic Theory of Gases: Kinetic Theory Of Gases Worksheets
Simulations and visualizations are powerful tools that can be used to help students understand the kinetic theory of gases. These tools allow students to see the behavior of gases at the molecular level, which can help them to develop a deeper understanding of the concepts involved.
There are a number of different simulations and visualizations that are available online. Some of the most popular include:
- The PhET Interactive Simulations from the University of Colorado Boulder
- The Molecular Workbench from the Concord Consortium
- The GasLab from the University of California, Berkeley
These simulations and visualizations can be used to demonstrate a variety of concepts related to the kinetic theory of gases, including:
- The relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature
- The distribution of molecular speeds
- The behavior of gases in different containers
- The effects of temperature on the rate of diffusion
Simulations and visualizations can be a valuable tool for teaching the kinetic theory of gases. They can help students to visualize the behavior of gases at the molecular level, which can lead to a deeper understanding of the concepts involved.
Resources for Teaching Kinetic Theory of Gases
The kinetic theory of gases is a fundamental concept in physics that explains the behavior of gases in terms of the motion of their constituent particles. There are numerous resources available to assist in teaching this topic effectively.
These resources provide a range of materials, including textbooks, articles, websites, and simulations, that can be tailored to different learning styles and levels.
Books
- Kinetic Theory of Gases by C. Kittel and H. Kroemer: A comprehensive textbook that covers the fundamentals of kinetic theory, including derivations and applications.
- An Introduction to the Kinetic Theory of Gases by J. Jeans: A classic text that provides a historical perspective and in-depth treatment of the subject.
- Statistical Physics by F. Reif: A more advanced textbook that explores the statistical basis of kinetic theory and its applications in other areas of physics.
Articles
- The Kinetic Theory of Gases by R. Resnick and D. Halliday: A concise article that provides an overview of the basic principles of kinetic theory.
- Applications of Kinetic Theory to Real Gases by J. Hirschfelder, C. Curtiss, and R. Bird: An article that discusses the applications of kinetic theory to understanding the behavior of real gases.
- The Kinetic Theory of Gases: A Historical Perspective by S. Brush: An article that traces the development of kinetic theory from its early beginnings to its modern form.
Websites
- Hyperphysics: A website that provides interactive simulations and animations to illustrate the concepts of kinetic theory.
- Khan Academy: A website that offers video lectures and practice exercises on kinetic theory.
- The Physics Classroom: A website that provides a variety of resources on kinetic theory, including simulations, worksheets, and quizzes.
Other Materials, Kinetic theory of gases worksheets
- Simulations: Simulations can provide students with a visual representation of the motion of gas particles and help them understand the relationship between particle properties and gas behavior.
- Experiments: Hands-on experiments can allow students to observe the behavior of gases directly and test the predictions of kinetic theory.
- Demonstrations: Demonstrations can be used to illustrate the concepts of kinetic theory in a visually engaging way.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are kinetic theory of gases worksheets?
Kinetic theory of gases worksheets are interactive learning materials that explore the principles and applications of kinetic theory of gases, providing a hands-on approach to understanding gas behavior.
How can I use kinetic theory of gases worksheets in my teaching?
Kinetic theory of gases worksheets can be incorporated into lessons to enhance student engagement and deepen their understanding of gas behavior. They provide opportunities for students to apply concepts and develop problem-solving skills.
Where can I find reputable kinetic theory of gases worksheets?
Numerous reputable websites and educational platforms offer high-quality kinetic theory of gases worksheets. These resources have been developed by experts and are designed to support effective learning.